/*
1.In computer programming, a loop is a sequence of
instructions that is repeated until a certain condition is reached.
2.An operation is done, such as getting an item of data and
changing it, and then some condition is checked such as whether
a counter has reached a prescribed number.
3.Counter not Reached: If the counter has not reached the
desired number, the next instruction in the sequence returns
to the first instruction in the sequence and repeat it.
4.Counter reached: If the condition has been reached,
the next instruction “falls through” to the next sequential
instruction or branches outside the loop.
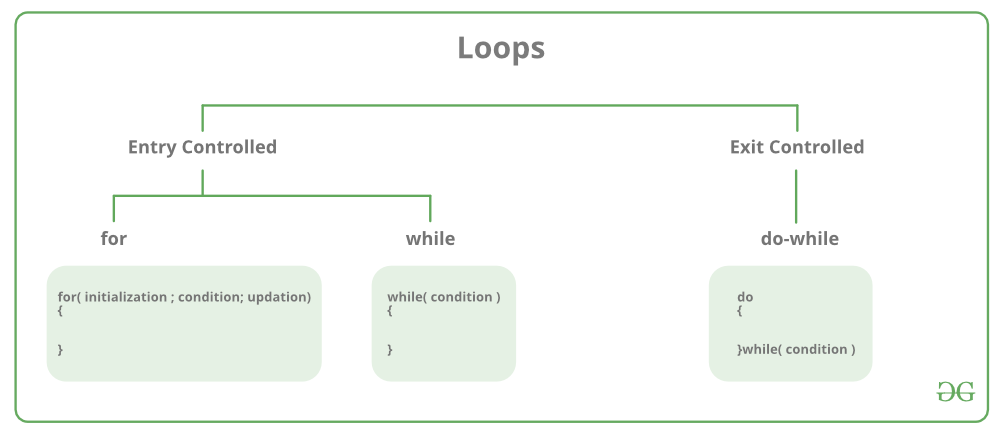
There are mainly two types of loops:
1.Entry Controlled loops: In this type of loops the test
condition is tested before entering the loop body.
For Loop and While Loop are entry controlled loops.
2.Exit Controlled Loops: In this type of loops the test
condition is tested or evaluated at the end of loop body.
Therefore, the loop body will execute at least once,
irrespective of whether the test condition is
true or false. do – while loop is exit controlled loop.
*/
Comments
Post a Comment